If you’ve ever applied for a new loan or credit card, then you probably already know that credit checks can impact your credit score and cause marks known as “credit inquiries” to appear on your credit reports.
There are two types of credit inquiries: hard and soft. Soft inquiries (also known as soft pulls or soft credit checks) don’t affect your credit score, and unlike hard inquiries, they can be conducted by companies without your permission. Read on to learn all about soft inquiries and what it means if you have one on your credit report.
Table of Contents
How does a soft inquiry work?
Any time anyone (including you) requests a copy of your credit report from one of the major credit reporting agencies, that request is recorded in your credit history as a credit inquiry. Think of these inquiries as a record of who’s viewed your credit report and why.
Each inquiry falls into one of two categories:
- Hard inquiries: Also called hard pulls, these are typically associated with applications for new credit. If you apply for a credit card or loan, your potential lender will conduct a hard inquiry.
- Soft inquiries: Soft pulls are credit checks that don’t result from an application for credit. If you check your own credit (or if another company checks it without getting your permission, e.g., to see if you prequalify for one of their credit cards), it will show up as a soft inquiry.
Importantly, while hard inquiries drop your credit score by several points, soft inquiries don’t affect your credit score at all.
Why don’t soft inquiries hurt your credit score?
Research has shown that people who are actively applying for credit tend to be a greater risk to lenders. Trying to open a lot of new credit accounts suggests that you might be financially struggling.
This is why credit scoring companies like FICO and VantageScore use hard inquiries (which come from credit applications) to calculate your credit score and predict your risk as a borrower. 1
Conversely, soft inquiries don’t predict risk in the same way. Checking your own credit doesn’t suggest anything bad about your finances. For this reason, soft inquiries aren’t included in credit scoring algorithms.
The graphic below shows the differences between soft and hard credit checks in detail:
Soft Inquiries vs. Hard Inquiries

What do soft inquiries look like on your credit report?
Soft inquiries can appear on your Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion credit reports. Each of the three major credit bureaus has its own set of credit reporting codes, so soft inquiries can appear on your credit reports in a number of ways (listed in the table below).
Soft inquiries will be listed in a clearly marked section of your credit report. It might be labeled “Account Inquiries,” “Who Has Viewed Your Consumer Information,” or something similar.
Some soft inquiries look similar to other (hard) inquiries, displaying the name of the lender or company that pulled your report. Others may look different, particularly if you triggered the soft pull by checking your own report.
Soft inquiries may appear under any of the following names or codes on your credit report:
Common Soft Inquiry Codes
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Equifax/Experian/TransUnion | One of the credit bureaus checked your credit report, either by your request or by a third party’s. |
| Factact Free Disclosure/FACTACT | Factact Free Disclosure indicates you checked your own credit (per your rights as a consumer under the FACT Act). |
| Consumer report/CONS RPT | You checked your credit report or authorized another company to do it. |
| Company name | The company in question checked your credit for reasons other than you applying for credit. |
| AM/AR | One of your current creditors reviewed your credit history. |
| CAR RENT | A car rental company checked your credit after you conducted a transaction with them. |
| COLLECT | A creditor or debt collector checked your credit for reasons related to an outstanding debt that you owe. |
|
|
|
As you can see, many of these codes come from prequalification checks for different types of credit. These count as soft inquiries, not hard inquiries, because creditors can try to prequalify you without your consent. You’ll only get a hard pull when you actively apply for credit on your own.
Examples of soft pulls on credit reports
The images below show how soft inquiries actually appear on two consumer credit reports (from TransUnion and Experian, respectively).
TransUnion Soft Inquiries

The consumer requested the first two soft pulls themselves, which is why they show up under FACTACT and the consumer’s own name (written as YOUR NAME in this image). The second two soft inquiries were performed by third-party companies (an insurance company and a stockbroker) for underwriting purposes.
Experian Soft Inquiries
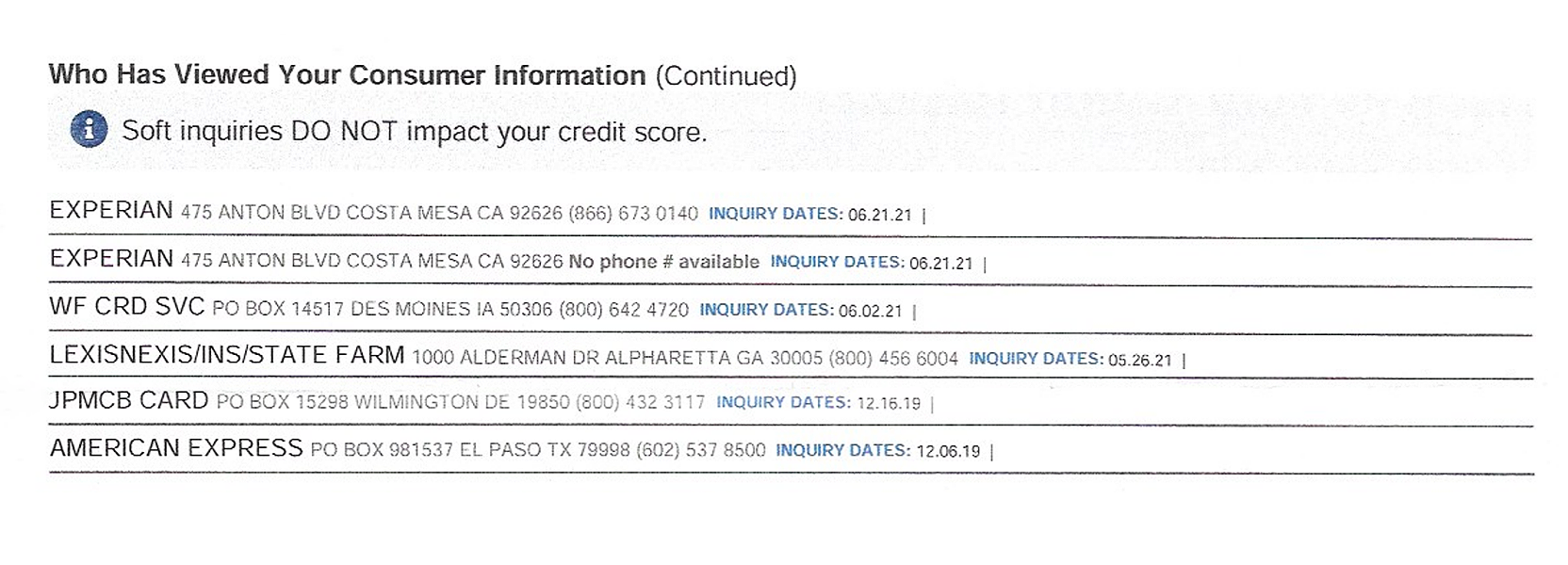
This credit report also shows several self-checks (the first two, labeled Experian, were requested by the consumer). The remainder were conducted by third-party companies.
The codes that companies appear under can sometimes be hard to decipher. For instance, in this image, JPMCB Card stands for JPMorgan Chase Bank Card, meaning that JPMorgan Chase Bank evaluated this consumer for prequalification. However, that isn’t apparent from the inquiry itself unless you’re already familiar with the JPMCB acronym.
Can lenders see soft pulls on your credit report?
No, soft inquiries don’t appear on the credit reports that lenders use to evaluate your creditworthiness. 2 Lenders can’t see them.
You’ll be able to see soft inquiries on your own report, but you don’t need to worry about them affecting your application for a mortgage, credit card, or any other credit account.
How long do soft inquiries stay on your credit report?
All credit inquiries—whether hard or soft—will stay on your credit report for a maximum of 2 years. 3 Some soft inquiries may even be removed from your credit report after just 1 year. 2
Do you need to remove soft inquiries from your credit report?
No, it isn’t necessary to take steps to remove soft inquiries early, since they don’t hurt your credit. It’s sometimes a good idea to remove hard inquiries from your credit report (especially if they were included on your report by mistake), but soft inquiries can’t hurt you, no matter how many of them you have.
What information does a soft credit check show?
In most cases, soft credit checks provide the same information as hard credit checks. This includes an overview of the following information in your credit report:
- Personal identifying information, such as your name and address
- Credit account information (e.g., your payment history and types of credit accounts you have)
- A list of past hard inquiries
- Public records (e.g., bankruptcies)
Note that depending on what kind of company is checking your credit, they might also pull other information from different sources.
For example, a landlord running a credit check on you may get your report from a background screening company that also provides your credit score and information about your eviction history.
By contrast, a prospective employer probably wouldn’t see that information when running an employment credit check.
Who can run a soft credit check?
Not just anybody can run a credit check on you. Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act, an individual or business must prove that they have a “permissible purpose” for checking your credit. 4
A company can run your credit if they’re genuinely checking whether you qualify for their services or have a legitimate need to conduct a background check on you. However, they can’t check your credit if they’re not considering a business relationship with you at all.
With that said, companies don’t need to ask your permission before running soft credit checks. 5 For example, creditors may pull your report to preapprove you for a new credit card without getting your consent.
The following are all examples of people or organizations that can conduct a soft pull:
- You
- Lenders (e.g., credit card issuers, auto loan providers, mortgage lenders, and banks/financial institutions)
- Credit monitoring service providers
- Landlords and property management companies
- Employers
- Insurance companies
- Leasing/rental companies
- Government agencies
- Background check/screening companies
- The Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
If you don’t want credit card companies or other creditors pulling your credit report to preapprove you for credit offers, you can have your name removed from preapproved offer mailing lists by visiting OptOutPrescreen.com or calling 1-888-567-8688 (1-888-5-OPTOUT).
You can opt out of receiving preapproval credit offers
How can you run a soft credit check on yourself?
Any time you view your own credit report, it’s treated as a soft credit check. You can get copies of your credit reports for free at AnnualCreditReport.com, which is a completely safe website that’s federally approved to provide credit reporting services.
You’re legally entitled to receive one free copy of your credit report per year (currently one per week until January 2023 due to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic).
In addition to pulling your actual credit report, you can also check your credit score, which can be done an unlimited number of times. If you have a credit card or bank account, you might be able to get your FICO score through your online portal. Alternatively, you can get your score from FICO’s website, although this will cost money.
Checking your credit score won’t lower it any more than pulling your credit report will. In fact, regularly checking your credit score and credit reports is key to building and maintaining a good credit score.
Takeaway: Soft credit checks occur when someone reviews your credit report but you haven’t applied for new credit.
- Credit checks can be “soft” or “hard.” Hard pulls are related to credit applications and hurt your credit score, whereas soft pulls do not.
- Examples of when soft credit checks occur include when you check your own credit report, a creditor preapproves you for an offer, or an employer checks your credit history.
- Soft pulls generally show the same information as hard pulls, including your personal information, account history, hard inquiries, and public records.
- To perform a soft credit check on yourself, all you need to do is request a copy of your credit report from one of the main credit bureaus.
- You can see soft inquiries on your credit report, but future lenders won’t be able to see them when reviewing your credit history.







